The Process
Step 1: Carbon Dioxide Enters the Leaf
One molecule of CO2 enters a mesophyll cell via a stoma.
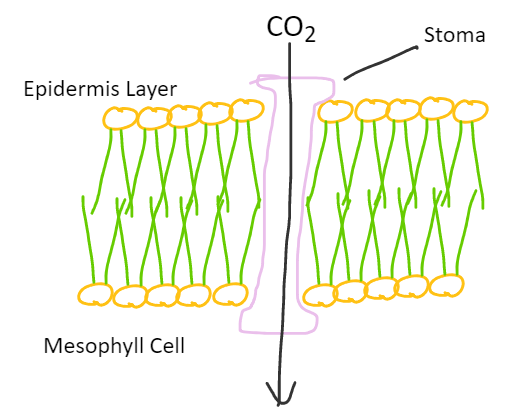
Step 2: Carbon Dioxide and Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) React
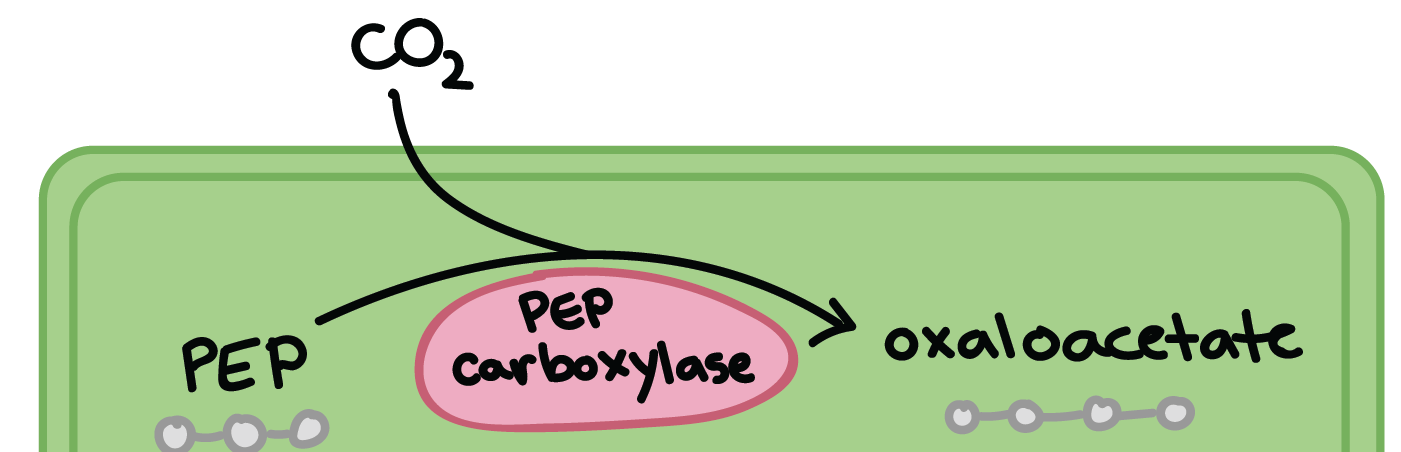
The CO2 that just entered the cell then reacts with PEP in the enzyme PEP carboxylase. The
PEP is a 3 carbon molecule, and fixing one CO2 molecule onto it will synthesize the 4 carbon
molecule, oxaloacetate.
PEP Carboxylase has no affinity for oxygen, so it will not react with it even if the oxygen is present in the cell.
PEP Carboxylase has no affinity for oxygen, so it will not react with it even if the oxygen is present in the cell.
Step 3: The Oxaloacetate is Converted to Malate
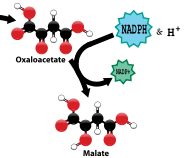
Using the products of the light dependent reactions, NADPH and H+, Oxaloacetate is converted
to Malate, which is also a 4 carbon molecule. This process releases NADP+ back to the light
dependent reactions. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme malate dehydrogenase.
Step 4
The Malate enters a bundle-sheath cell via a tube called plasmodesmata. This tube connects
bundle-sheath and mesophyll cells.
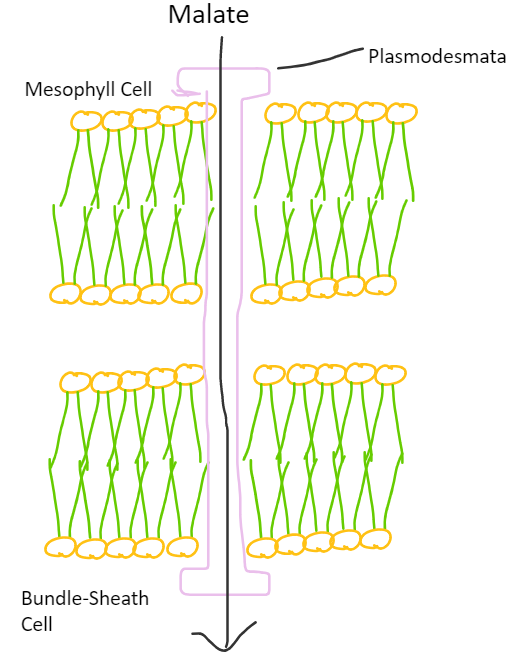
Step 5
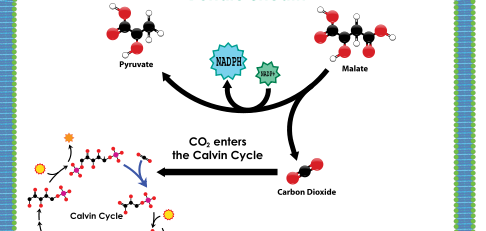
Once in the bundle-sheath cell, the malate splits into one molecule of carbon dioxide and
one molecule of pyruvate, a 3 carbon molecule. In the process, malate reduces NADP+ to NADPH
with the portion left after the carbon dioxide breaks off. The carbon dioxide then enters
the Calvin Cycle to complete the light independent reactions. The Calvin Cycle uses the
CO2 and refixes it using the Rubisco Enzyme. This produces 1 G3P molecule per
turn, so needs 2 cycles to synthesize one molecule of glucose.
Step 6: The Pyruvate Enters the Mesophyll Cell
The Pyruvate is transported into the mesophyll cell via a second plasmodesmata.
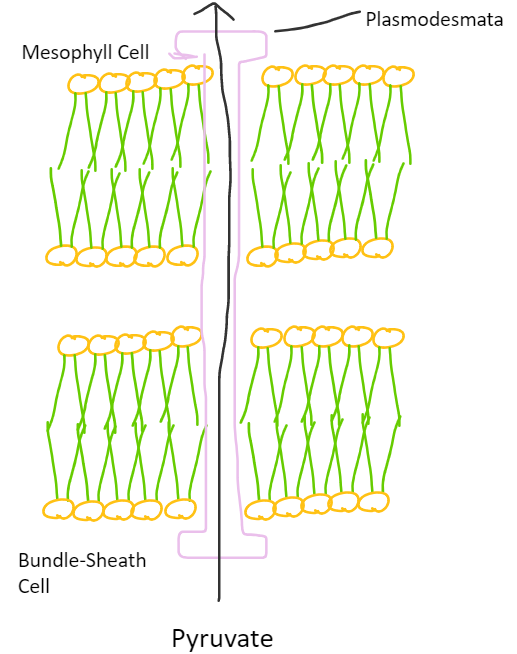
Step 7: The PEP is Regenerated
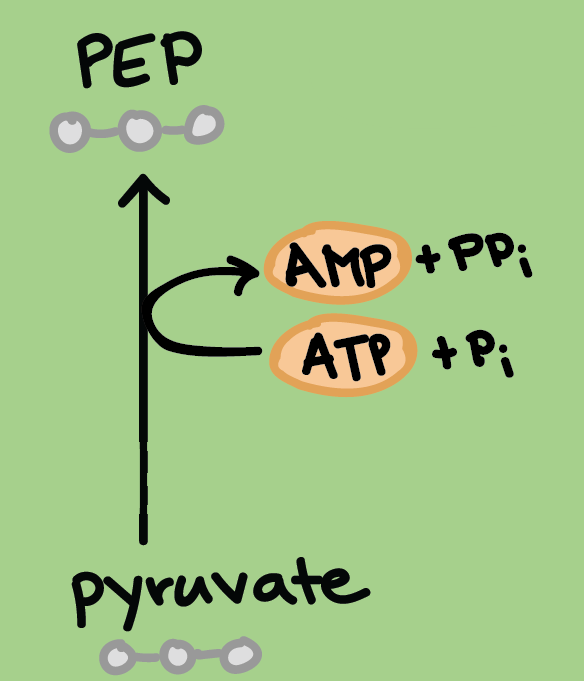
The Pyruvate reacts with a molecule of ATP and an inorganic phosphate group to regenerate
PEP and release Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) and two inorganic phosphate groups as
products. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme, phosphopyruvic dikinase.